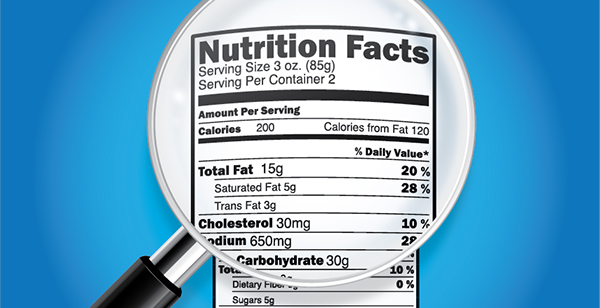
Understanding food labels is essential for making informed choices about the products we consume. Food labels provide valuable information about the nutritional content, ingredients, and serving sizes of packaged foods. In this article, we will explore how to navigate food labels effectively to make informed and healthier choices.
1. Serving Size:
Start by checking the serving size listed on the label. This information is crucial as all the nutrient values provided on the label are based on this serving size. Be mindful of portion sizes to accurately assess the nutritional content you consume.
2. Calories and Nutrients:
Look for the calorie content and the amounts of key nutrients such as fat (including saturated and trans fats), cholesterol, sodium, carbohydrates, fiber, sugars, and protein. Compare these values to your nutritional needs and dietary goals.
3. % Daily Value (%DV):
The %DV indicates how much of a specific nutrient is provided in one serving, relative to the recommended daily intake. Aim for foods that are lower in saturated fat, trans fat, cholesterol, and sodium, while higher in dietary fiber, vitamins, and minerals.
4. Ingredient List:
Read the ingredient list to understand what goes into the product. Ingredients are listed in descending order by weight, with the highest quantity first. Choose foods with shorter ingredient lists and avoid those with added sugars, artificial additives, and unhealthy fats.
5. Added Sugars:
Identify the amount of added sugars in the product. Added sugars contribute to excess calorie intake and can have negative health effects. Be cautious of different names for added sugars such as corn syrup, dextrose, sucrose, and others.
6. Allergens:
Check for allergen warnings if you have food allergies or sensitivities. Manufacturers are required to clearly state if a product contains common allergens such as peanuts, tree nuts, soy, wheat, dairy, or shellfish.
7. Claims and Labels:
Be aware of claims and labels on the packaging. Terms like “fat-free,” “low sodium,” or “high fiber” may be used for marketing purposes. However, it’s important to verify the nutrient content and compare it with your dietary needs.
8. Country of Origin:
If knowing the origin of your food is important to you, look for the country of origin label. It indicates where the food was grown, produced, or processed.
9. Organic and Sustainable Labels:
For those interested in organic or sustainable foods, look for official labels such as USDA Organic, Non-GMO Project Verified, or Fair Trade Certified. These labels indicate specific standards and practices that align with organic or sustainable principles.
10. Educate Yourself:
Stay informed about nutrition and food-related topics. Understand the basic principles of a healthy diet and the role of specific nutrients in your overall well-being. This knowledge will help you interpret food labels more effectively.
Navigating food labels is crucial for making informed choices about the foods we consume. By understanding serving sizes, assessing calorie and nutrient content, reading ingredient lists, and being aware of claims and labels, we can make healthier decisions. Remember to consider your individual dietary needs and goals when interpreting food labels. With practice and knowledge, you can confidently navigate food labels and make choices that support your overall health and well-being.
